so… neural networks are now at the core of every cool new AI product from “vizcom” to “stable diffusion” to “chatgpt” to “sora” to “gemini” and the reason for that is Neural Networks can Learn (almost) Anything
this blog post is intended to be a breakdown on the how, which involves diving into understanding how neurons form networks to learn. Most “How do Neural Network Work” resourses online focus on explaining backpropagation, understandable because backprop is pretty complication to get your head wrapped around
So How do Neural Networks Learn
there are 3 pieces you’ll need to understand to understand how neural networks learn
- Neurons
- How Neurons Network to Learn [Universal Approximation Theorem]
- Backpropagation
Neurons
y’all prolly already know this pretty well so i’m going to skim through ASAP
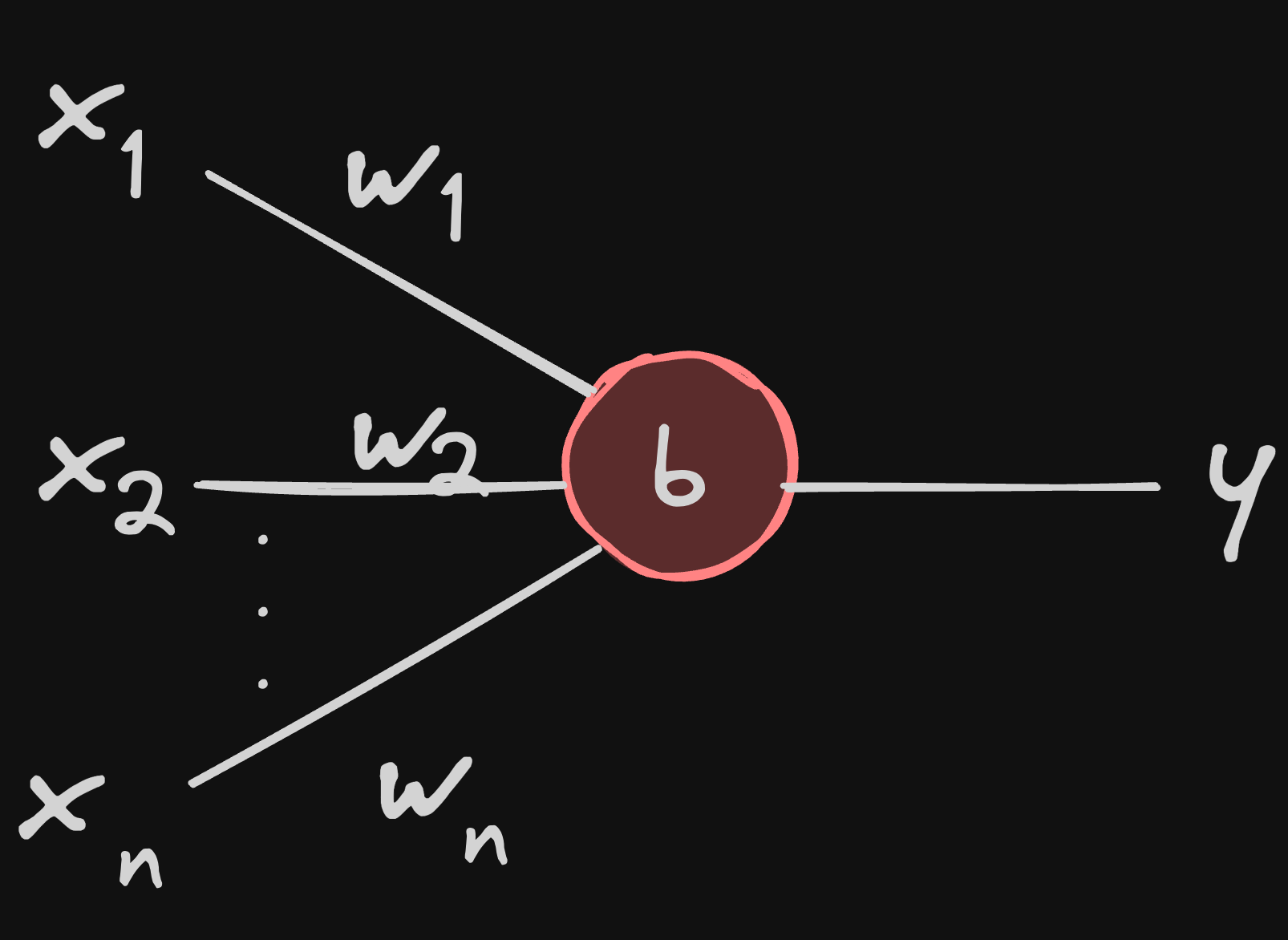
note: b is basically w0
a neuron is a mathematical model designed to make decisions in a very similar fashion to the biological neuron, There are 3 things you need to know about it
- input: sums up all of it’s input values
- activation function: a function that activates the neuron’s decision when the sum of inputs crosses a threshold
- output: the decision on the neuron, 1 implies yes, 0 implies no
- weights: the importance a input to a neuron
- bias: the importance of the neuron in the network
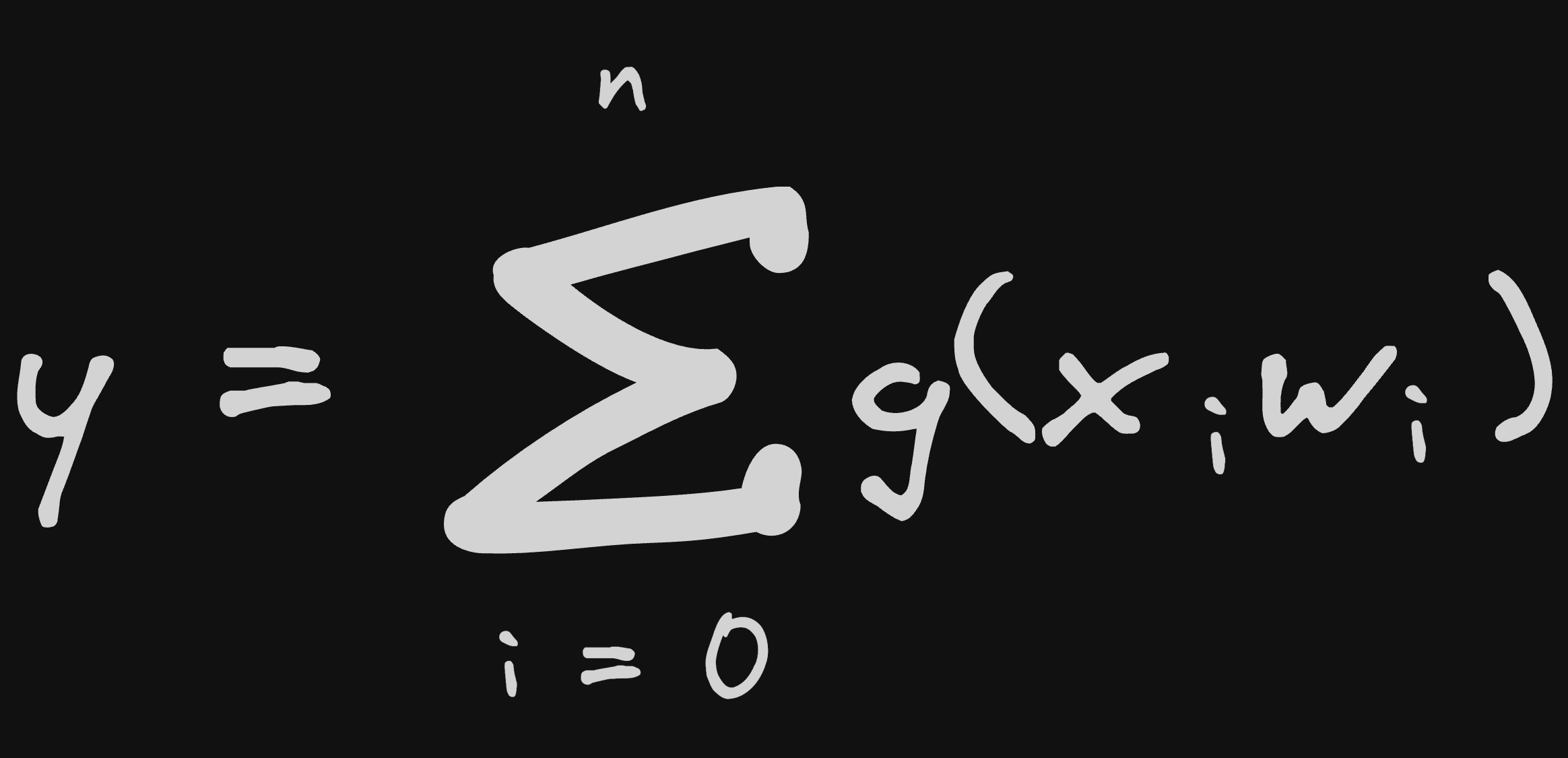
there’s a lot of cool things to discuss when it comes to the intution behind activation functions, a separate blog post on it maybe…
How Neurons Network to Learn
let’s try to understand what actually happens when 2 neurons form a network, and how they learn…
 a neuron (a visual representation)
a neuron (a visual representation)
this is a neuron as we know it, but actually it is better to look at it as the graph of the function it represents
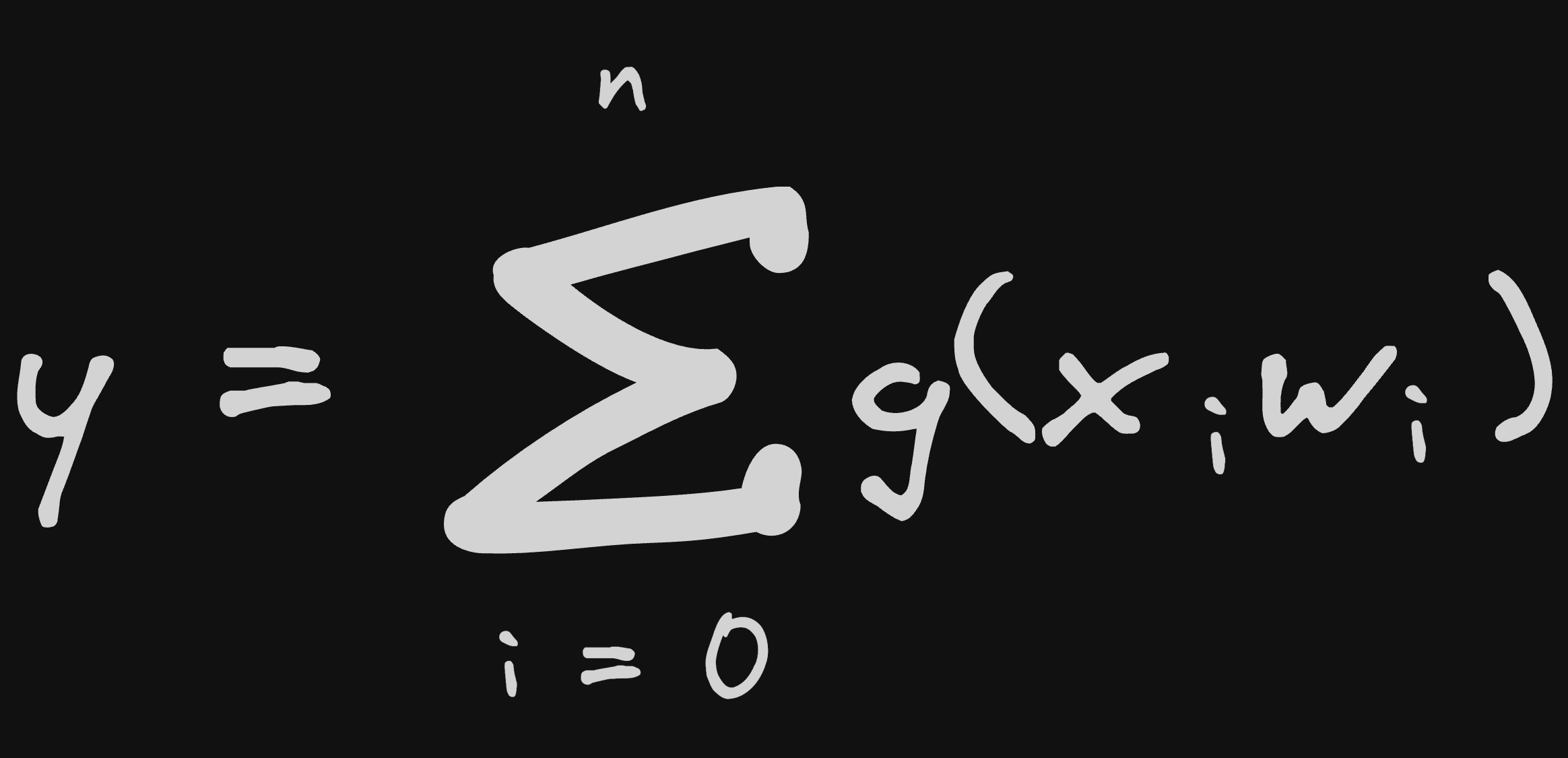 a neuron (the function it represents)
a neuron (the function it represents)
assuming g(x) is a step function
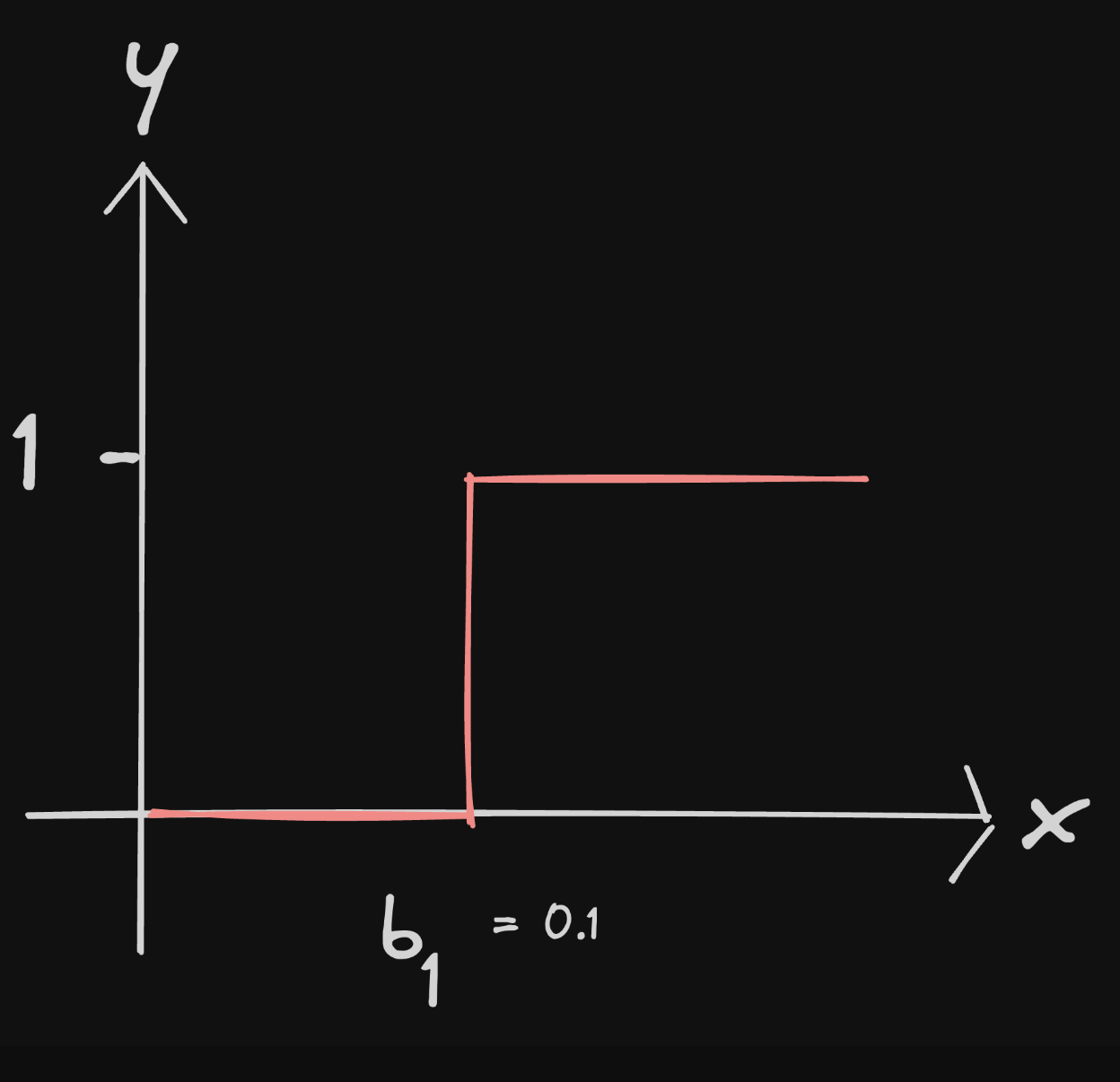 a neuron (the graph output of the function it represents)
a neuron (the graph output of the function it represents)
What Happens When 2 Neurons form a Network
assume 2 neurons with a step activation function
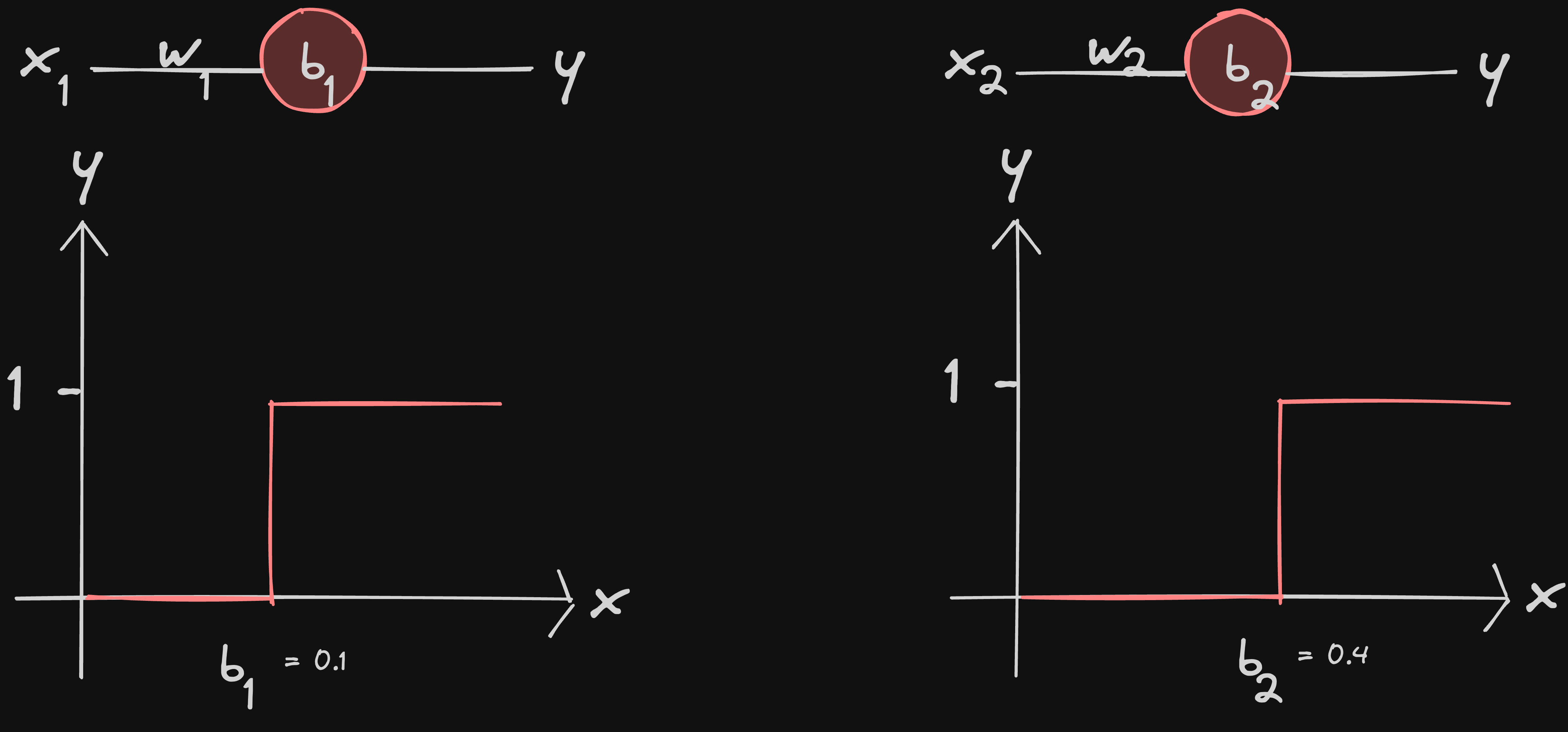
now let’s try to visualize a neural network out of these 2 neurons… we can do this by introducing another neuron
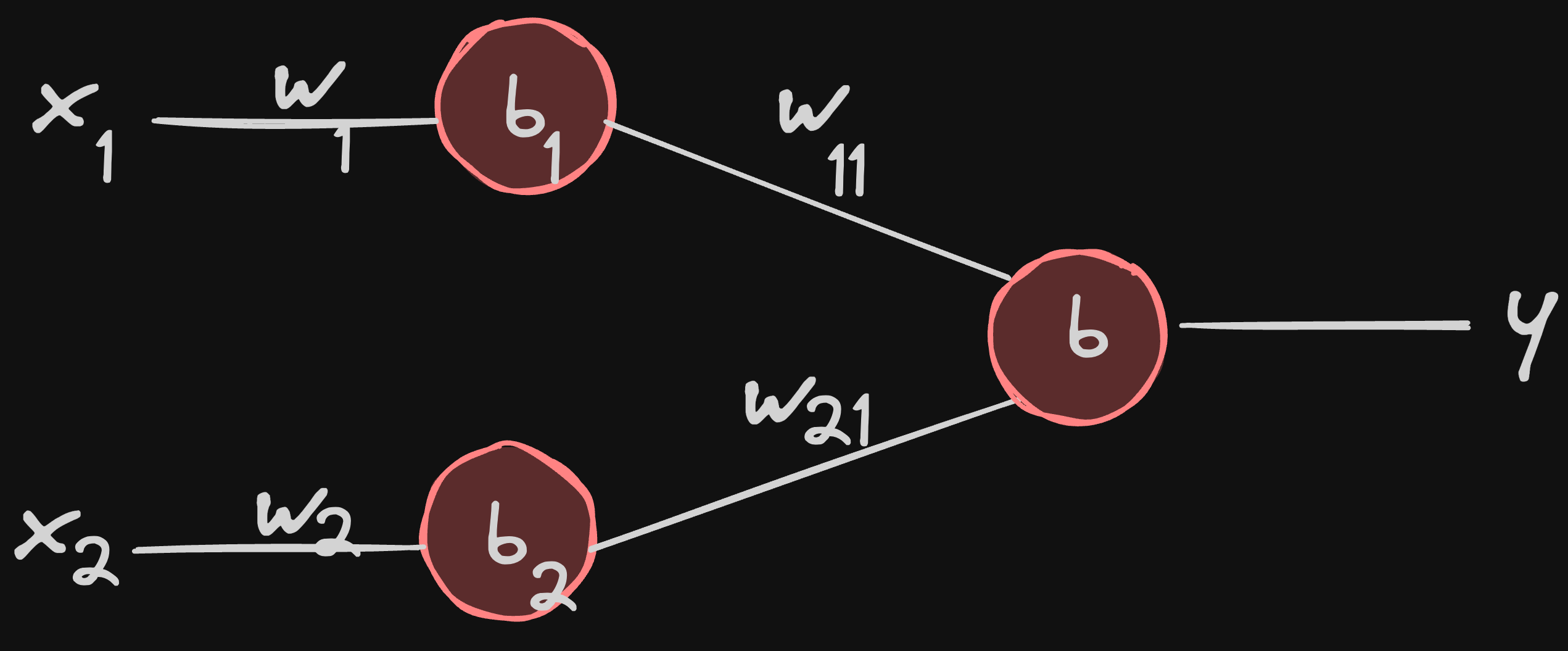
we can control the output of the network by tweaking the value of w11 and w21
let’s say b = 0 for simplicity purposes
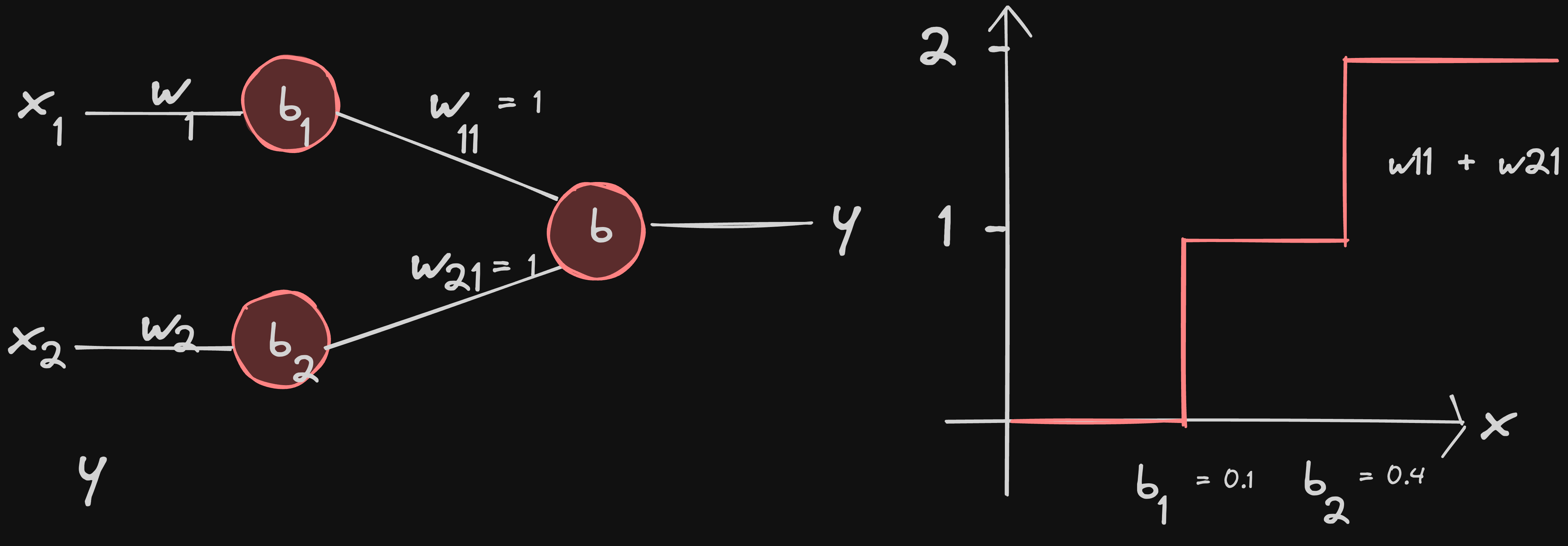 w11 = 1, w21 = 1 just adds both the graphs based on the principle of superposition
w11 = 1, w21 = 1 just adds both the graphs based on the principle of superposition
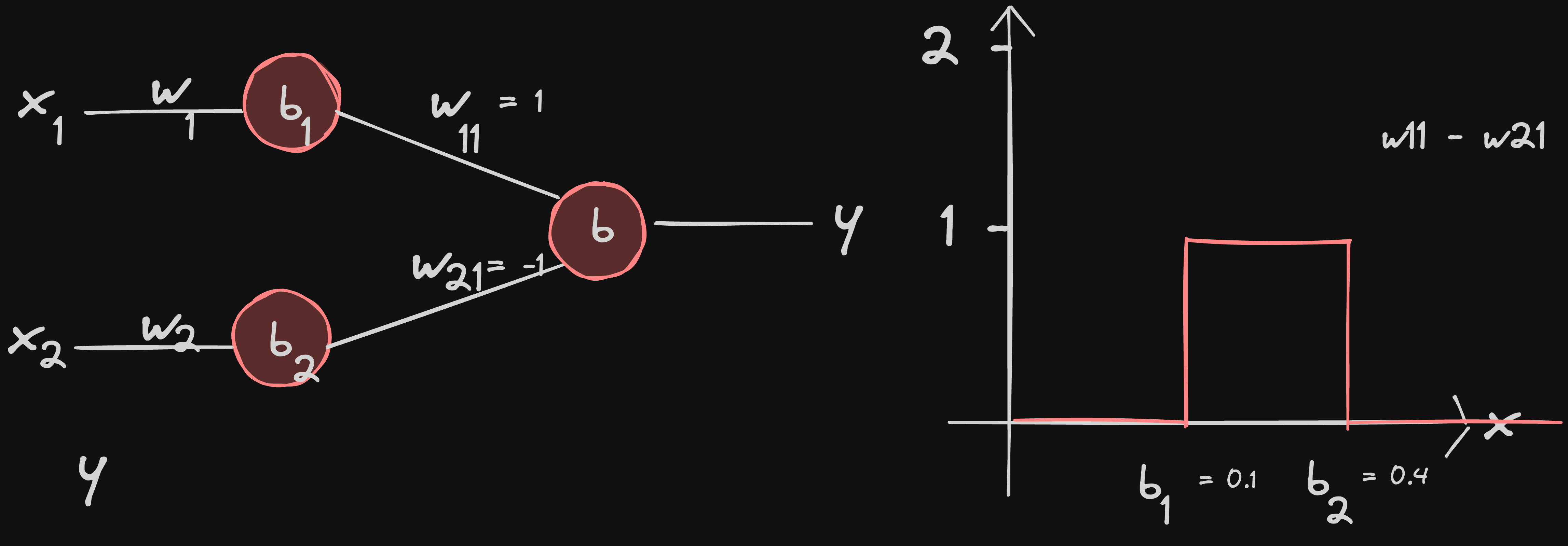 w21 = -1 inverts the graphs from neuron2 and adds the graph of neuron1 based on the principle of superposition
w21 = -1 inverts the graphs from neuron2 and adds the graph of neuron1 based on the principle of superposition
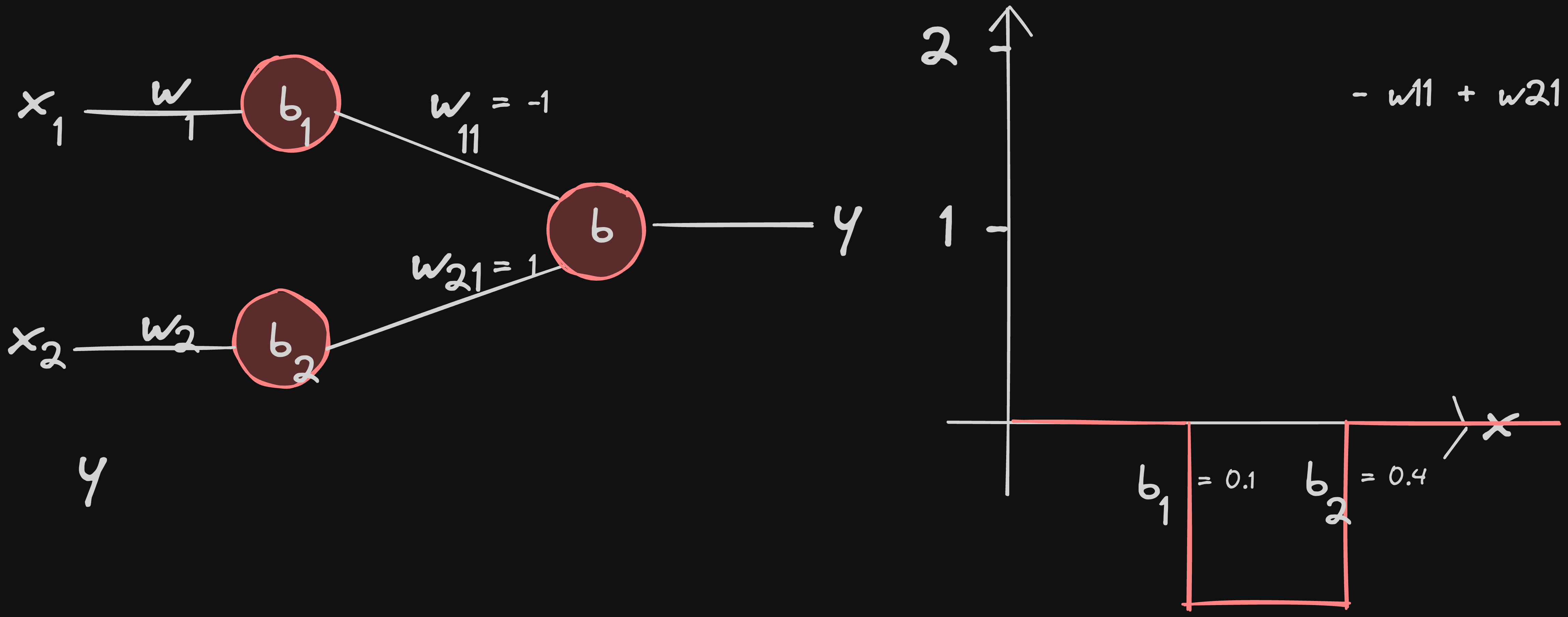 w11 = -1 inverts the graphs from neuron1 and adds the graph of neuron2 based on the principle of superposition
w11 = -1 inverts the graphs from neuron1 and adds the graph of neuron2 based on the principle of superposition
note: weight value basically just scales the function of a neuron
try drawing the graph for w11 = 1.5 and w21 = -0.5 [click to reveal answer]
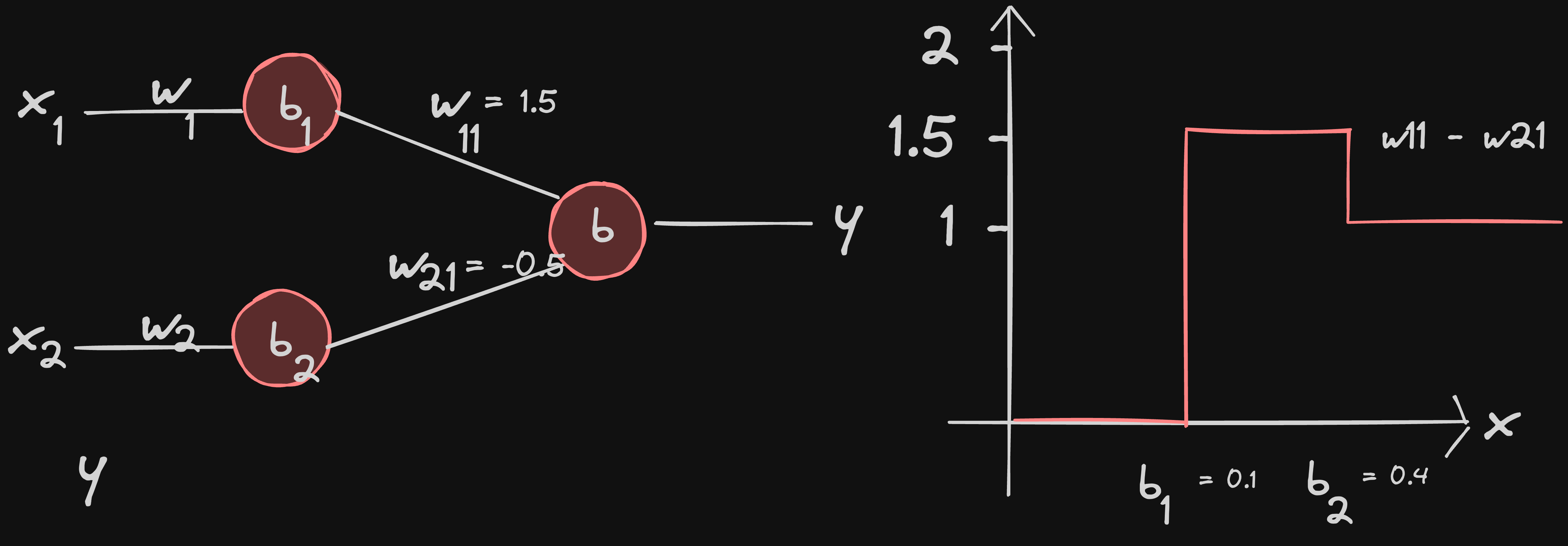
so when neural networks learn patterns, what they do that is, tweaking each the weights and biases of neuron so that the graph output traces the pattern to be learnt
in essense when neural networks learn they’re slowly trying to approximate functions
this way, neural networks can learn anything by approximately tracing the mathematical representation of what we’re trying to teach the network…
a neural network with at least one hidden layer of a sufficient number of neurons, and a non-linear activation function can approximate any continuous function to an arbitrary level of accuracy
Back Propagation
the final piece in grasping neural networks… with UAT, we understood what/how tweaking weights and biases help the neural network learn any pattern
now with Back Propagation, we shall understand how a neural network automatically tweaks it’s own weights and biases to learn the pattern
until next time !️ ✌
or you could spot me in the wild 🤭 i mean instagram, twitter, linkedin and maybe even youtube where i may make video versions of these blog posts